The concept of hybrid vehicles, blending a traditional internal combustion engine with an electric motor, is not a novel idea. In fact, some hybrid automobiles were produced over a century ago to address the limited range of early electric vehicles and the difficulty in starting the primitive internal combustion engines. However, the hybrid technology remained dormant until the 1970s, when the dramatic rise in gasoline prices exposed the inherent inefficiency of relying solely on internal combustion engines in cars.
As automotive engineers began searching for more efficient alternatives, the hybrid-car concept resurfaced as a promising solution. Researchers and students started exploring strategies for designing and constructing various prototype hybrid vehicles, uncovering the unique challenges in engineering these advanced powertrains. Chief among these challenges were the need for efficient and lightweight energy-storage devices, effective computer management systems, and efficient transmission systems to harmonize the dual power sources.
The hybrid revolution was fueled by the desire to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, ultimately leading to the development of increasingly eco-friendly transportation options that prioritize sustainable mobility. The technological advancements in battery technology and regenerative braking systems, exemplified by models like the Toyota Prius, have been instrumental in shaping the evolution of hybrid cars and plug-in hybrids and their growing popularity among modern drivers seeking hybrid powertrain solutions and EV tax credits.
Key Takeaways
- The hybrid vehicle concept, combining a conventional engine and an electric motor, has existed for over a century, but gained renewed interest in the 1970s due to rising gasoline prices.
- Automotive engineers and researchers faced challenges in developing efficient hybrid powertrains, including the need for advanced energy-storage devices, computer management systems, and transmission systems.
- Hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles have evolved to offer improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and sustainable mobility solutions for modern drivers.
- Advancements in battery technology and regenerative braking have been crucial in the development of hybrid and plug-in hybrid models, such as the Toyota Prius.
- Government incentives, including EV tax credits, have further encouraged the adoption of hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles as eco-friendly transportation options.
The Evolution of Hybrid Vehicles
The first hybrid vehicles were designed to address the limited range of existing electric vehicles and the difficulty of starting the early internal combustion engines, which had to be cranked by hand. These early hybrid vehicles, along with the purely electric cars that dominated the fledgling automobile industry in the early 20th century, eventually gave way to a proliferation of cars based on the now-ubiquitous internal combustion engine, made possible by the relatively low cost and widespread availability of gasoline.
Resurgence of Hybrids in the 1970s
The hybrid concept remained dormant until the 1970s, a decade during which the price of gasoline tripled. The higher cost brought to light the inherent inefficiency of using internal combustion engines in cars, such as engines idling while the car is stopped and power being wasted through throttling. Automotive engineers began to search for better alternatives, and the hybrid-car concept looked quite interesting.
Overcoming Technological Challenges
Researchers and students started exploring strategies for designing and constructing various prototype hybrid vehicles, which revealed the challenges of engineering hybrid vehicles. These challenges included the need for efficient and lightweight energy-storage devices, effective computer management systems to efficiently deliver power to the wheels and regenerate energy during braking, and efficient transmission systems to handle more than one power plant.
How Hybrid Cars Work
Hybrid cars are a unique blend of traditional gasoline-powered vehicles and cutting-edge electric technology. These innovative automobiles combine a gasoline-fueled internal combustion engine with an electric motor and a rechargeable battery pack, harnessing the strengths of both power sources to deliver exceptional fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
Combining Gasoline and Electric Power
At the heart of a hybrid car’s design is the seamless integration of the internal combustion engine and the electric motor. The gasoline engine is responsible for charging the battery and providing additional power when needed, while the electric motor takes over during low-speed or all-electric driving conditions. This synergistic relationship allows hybrid cars to optimize power delivery and minimize fuel consumption, resulting in a significantly more efficient driving experience compared to traditional gas-powered vehicles.
Regenerative Braking Systems
A key feature that enhances the efficiency of hybrid cars is the regenerative braking system. When the driver applies the brakes, the electric motor acts as a generator, capturing the kinetic energy that would otherwise be lost and using it to recharge the vehicle’s battery. This process not only helps to extend the battery’s range, but it also reduces the wear and tear on the conventional braking system, contributing to a more sustainable and cost-effective ownership experience.
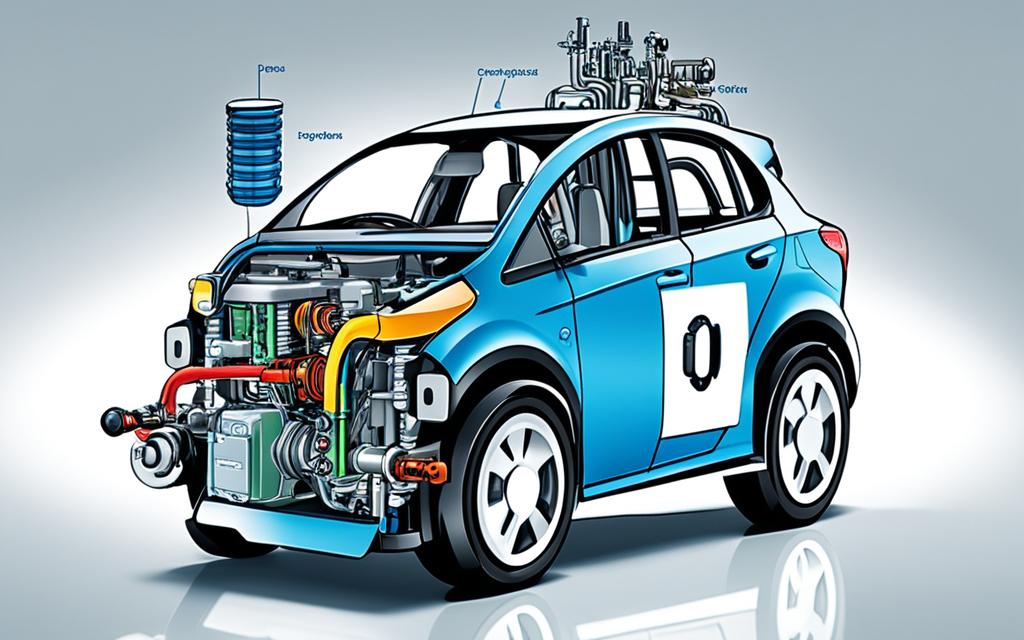
Hybrid Cars and Plug-In Hybrids
Hybrid cars and plug-in hybrids are two distinct types of vehicles that both combine gasoline and electric power, but with some key differences. Hybrid cars have a smaller battery pack and rely more on the internal combustion engine, while plug-in hybrids have a larger battery pack that can be recharged from an external power source, allowing them to drive longer distances in all-electric mode before the gasoline engine is needed.
The key distinction between these two types of hybrid vehicles lies in their battery capacity and reliance on the electric motor. Hybrid cars typically have a smaller battery pack that is primarily used to assist the gasoline engine, providing a boost in power and efficiency. In contrast, plug-in hybrids feature a larger battery pack that can be recharged from a wall outlet or public charging station, enabling them to operate in all-electric mode for a more extended range before the gasoline engine is required.
This difference in battery capacity and electric driving range has significant implications for the environmental impact and user experience of these vehicles. Plug-in hybrids, with their ability to drive longer distances on electricity alone, offer the potential for even greater reductions in fuel consumption and emissions compared to their hybrid counterparts. However, the higher battery capacity and availability of external charging also come with a higher purchase price for plug-in hybrid models.
Ultimately, both hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles represent important steps towards more sustainable transportation, offering drivers a blend of efficiency, performance, and environmental responsibility. As the technology continues to evolve, consumers will have an increasingly diverse range of options to choose from, catering to their specific driving needs and preferences.
Benefits of Hybrid and Plug-In Hybrid Vehicles
Hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles offer significantly improved fuel efficiency compared to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. The combination of an internal combustion engine and electric motor, along with features like regenerative braking, allow these vehicles to achieve higher miles per gallon ratings, reducing fuel consumption and costs for drivers.
Improved Fuel Efficiency
Hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles are designed to maximize fuel efficiency, delivering substantial savings at the pump. Their advanced powertrains, which seamlessly integrate gasoline and electric propulsion, enable these vehicles to achieve exceptional mileage, often doubling or even tripling the fuel economy of their conventional counterparts.
Reduced Emissions
Hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles have lower emissions than traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, as they emit fewer greenhouse gases and other pollutants. The ability to operate in all-electric mode, especially for plug-in hybrids, further reduces emissions and contributes to a more sustainable transportation solution, benefiting both the environment and public health.
Cost Savings
Owning and operating a hybrid or plug-in hybrid vehicle can result in significant cost savings for drivers. In addition to improved fuel efficiency, these vehicles may also be eligible for various government incentives and tax credits, which can help offset the initial purchase price, making them a more affordable and attractive option for eco-conscious consumers.

Varieties of Hybrid and Plug-In Hybrid Models
The hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicle market has expanded to encompass a diverse range of vehicle segments, catering to the varied needs and preferences of modern drivers. From compact and midsize cars to spacious SUVs and crossovers, and even capable pickup trucks, hybrid and plug-in hybrid options are now available across the automotive spectrum.
Compact and Midsize Cars
In the compact and midsize car categories, popular hybrid models include the Toyota Prius, Honda Accord Hybrid, and Hyundai Ioniq Hybrid. These vehicles strike a balance between efficiency, performance, and affordability, making them an attractive choice for eco-conscious consumers seeking a practical and sustainable transportation solution.
SUVs and Crossovers
The hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicle market has also expanded to include larger SUVs and crossovers, catering to those who require more space and utility. Models such as the Toyota RAV4 Hybrid, Ford Escape Hybrid, and Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV offer the spaciousness and capabilities of an SUV while delivering improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
Pickup Trucks
Hybrid and plug-in hybrid technology is even making its way into the traditionally gas-guzzling pickup truck segment. Models like the Ford F-150 Hybrid and the upcoming Chevrolet Silverado Hybrid provide the capability and hauling capacity of a traditional pickup, combined with the efficiency and sustainability benefits of hybrid powertrains.
Minivans
Hybrid options are also available in the minivan segment, with the Toyota Sienna Hybrid providing families with a fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly transportation solution without sacrificing space and functionality.
The Future of Hybrid Technology
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, the future of hybrid technology holds immense promise. Ongoing advancements in battery technology, such as improvements in energy density, power output, and charging capabilities, are expected to further enhance the performance and capabilities of hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles.
Advancements in Battery Technology
These technological improvements in battery technology will contribute to extended all-electric driving ranges and improved overall efficiency of hybrid powertrains. Drivers can anticipate even greater fuel savings and reduced emissions as hybrid vehicles become more capable of operating in all-electric mode for longer distances.
Integration with Autonomous Driving
As autonomous driving technology continues to develop, hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles are well-positioned to integrate these features seamlessly. The combination of efficient hybrid powertrains and advanced autonomous driving capabilities could lead to even greater improvements in fuel efficiency and emissions reduction. Automakers are exploring ways to leverage the synergies between hybrid technology and self-driving systems, paving the way for a more sustainable and intelligent transportation future.

Environmental Impact of Hybrids
Hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles have the potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and other pollutants compared to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. The ability to operate in all-electric mode, especially for plug-in hybrids, and the improved overall efficiency of the hybrid powertrain contribute to these environmental benefits.
Emissions Reduction Potential
By utilizing both electric and gasoline power, hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles are capable of dramatically reducing harmful emissions, such as carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. This is particularly true in urban environments where air quality is a significant concern. The all-electric driving range of plug-in hybrids allows for even greater emissions reduction potential, as drivers can complete their daily commutes without relying on the internal combustion engine.
Sustainability Concerns
While hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles offer significant environmental advantages, there are still sustainability concerns that need to be addressed. The production and disposal of the batteries used in these vehicles can have an impact on the environment, particularly in terms of resource extraction and the management of end-of-life battery systems. Ongoing research and development in battery technology, as well as the implementation of sustainable recycling and disposal processes, will be crucial in ensuring the long-term sustainability of hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles.
Charging Infrastructure for Plug-In Hybrids
Plug-in hybrid owners have the convenient option of charging their vehicles at home, using either a standard household outlet or a dedicated Level 2 charging station. This home charging solution provides a reliable and accessible way to maintain the vehicle’s battery charge, allowing drivers to take full advantage of the all-electric driving range.
Home Charging Solutions
Charging a plug-in hybrid at home is a simple and efficient process. Owners can utilize a standard 120-volt household outlet, often referred to as Level 1 charging, to gradually replenish the battery over several hours. For a faster charging experience, a dedicated Level 2 charging station, which operates on a 240-volt system, can be installed in the home, significantly reducing the time required to fully charge the vehicle.
Public Charging Stations
To support the growing number of plug-in hybrid and electric vehicles on the road, the availability of public charging stations is steadily expanding. These public charging facilities, including both Level 2 and DC fast charging options, provide additional charging opportunities for drivers, especially for longer commutes or road trips. The accessibility of these public charging stations helps to alleviate range anxiety and enables plug-in hybrid owners to confidently venture beyond the limits of their home charging setup.

Government Incentives and Regulations
Many governments around the world offer various incentives and tax credits to encourage the adoption of hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles. These financial incentives, such as federal and state tax credits, can help offset the initial purchase price of these vehicles, making them more accessible to a wider range of consumers.
Tax Credits and Rebates
In the United States, the federal government provides a tax credit of up to $7,500 for the purchase of a new plug-in hybrid or electric vehicle. Additionally, several states offer their own incentives, such as rebates or tax exemptions, further reducing the cost of these eco-friendly transportation options. These government-backed initiatives play a crucial role in making hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles more affordable and appealing to potential buyers.
Emissions Standards
Governments are also implementing stricter emissions standards and regulations, which are driving automakers to develop and produce more hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles. These regulatory measures are aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality, further incentivizing the transition to more sustainable transportation options. By setting ambitious targets for emissions reduction, policymakers are creating a favorable environment for the widespread adoption of hybrid and plug-in hybrid technologies.
Hybrid vs. Electric Vehicles
While hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles offer improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions compared to traditional gasoline-powered cars, they typically have a more limited all-electric driving range compared to fully electric vehicles (EVs). This range consideration is an important factor for consumers to weigh when choosing between hybrid and electric options.
Range Considerations
Hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles rely on a combination of a gasoline engine and an electric motor, which allows them to achieve higher fuel efficiency and lower emissions than traditional gas-powered cars. However, their all-electric range is often significantly less than that of fully electric vehicles, which are powered solely by a battery and an electric motor. Consumers who prioritize the ability to drive longer distances in all-electric mode may find that a fully electric vehicle better suits their needs.
Cost Comparisons
Hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles are generally more affordable than fully electric vehicles, both in terms of the initial purchase price and ongoing operating costs. This cost differential, along with government incentives and tax credits available for these vehicles, can make hybrid and plug-in hybrid options a more accessible choice for some consumers. However, the long-term fuel savings and reduced maintenance costs of fully electric vehicles may offset the higher upfront investment for some buyers.
| Feature | Hybrid/Plug-In Hybrid | Electric Vehicle |
|---|---|---|
| Driving Range | Typically 20-50 miles in all-electric mode | Typically 200-400 miles on a single charge |
| Fuel Efficiency | Significantly improved compared to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles | Highest fuel efficiency with no direct emissions |
| Initial Purchase Price | Generally less expensive than fully electric vehicles | Typically more expensive than hybrid/plug-in hybrid models |
| Maintenance Costs | Reduced compared to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles | Lowest maintenance costs due to fewer moving parts |
Conclusion
Hybrid and plug-in hybrid vehicles have evolved significantly since their early concepts, offering drivers a sustainable transportation choice that combines the benefits of gasoline and electric power. With a growing variety of models, improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and government incentives, these vehicles are becoming an increasingly popular option for modern drivers seeking eco-friendly and cost-effective mobility solutions.
As technology continues to advance, hybrid powertrains are poised to play a crucial role in the transition towards a more sustainable transportation future. Ongoing advancements in battery technology, integration with autonomous driving, and the expansion of charging infrastructure will further enhance the capabilities and appeal of these hybrid vehicles.
Ultimately, the rise of hybrid and plug-in hybrid cars represents a significant step towards a greener and more efficient transportation landscape. By embracing these innovative mobility solutions, we can collectively contribute to reducing our carbon footprint and paving the way for a more sustainable tomorrow.
